Background
The current crypto trading ecosystem is fragmented, with both centralized (CeFi) and decentralized (DeFi) platforms presenting inherent limitations.
Beyond individual constraints – such as custodial risks in CeFi or liquidity and UX challenges in DeFi – the lack of interoperability between these two spheres, and even within the DeFi landscape itself, significantly hinders seamless asset movement and unified user experience across the broader digital asset economy.
Impermanent Loss.

Bridging the gaps
The Decentralized Order Book (DOB) project is at the crossroads of current CEX and DEX: the concept is to replicate centralized Market Making principles on the blockchain, using Decentralized Market Making Pools and layer 2 services, to build a hybrid type of exchange:
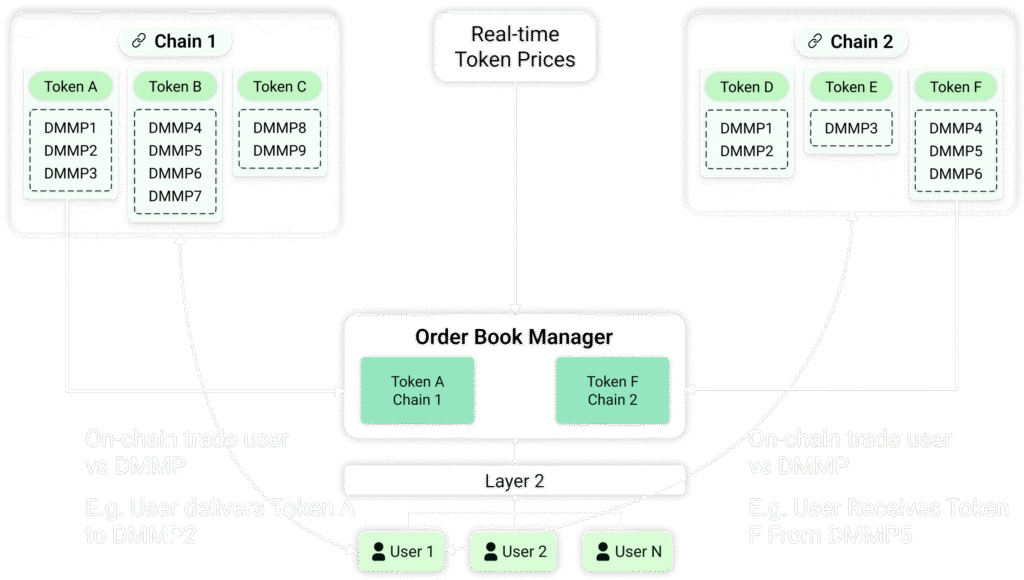
The Decentralized Order Book (DOB) developed by Asagaia addresses the critical limitations of both CeFi and DeFi by enabling high-frequency (HF) trading capabilities in a fully decentralized environment. The implementation is built around three key innovations:
While the system may not entirely eliminate impermanent loss (IL), it substantially mitigates its impact by enhancing liquidity and improving trade execution. This is achieved through
